The thoracic spine has a feature - the ribs connect it. Therefore, it is less mobile than the neck and lower back. Therefore, osteochondrosis in the thoracic region develops less frequently according to the following principle: "less mobility - less wear". But it develops less frequently - that doesn't mean it's easier to flow. It does. It's about chest pain. Because the pain area of the thoracic spine overlaps with the heart area, symptoms are often confused with angina or myocardial infarction. No wonder they say thoracic osteochondrosis is a "chameleon". After all, he could not only pretend to have a heart disease, but also a disease of the lungs, liver, stomach, gallbladder or pancreas. Here you can't make the mistake of ignoring a heart attack or other serious illness, such as the pathology of the female breast. A bug like this is costly, even if it will eventually be resolved. After all, this "drives" a person into serious stress. This is why it is important to find an experienced and knowledgeable doctor who will understand everything and differentiate the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis from other diseases. Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis generally fall into two categories - radicular and reflex.
radicular symptoms
They arise due to effects on the nerves that come out of the spine.
spinal nerve
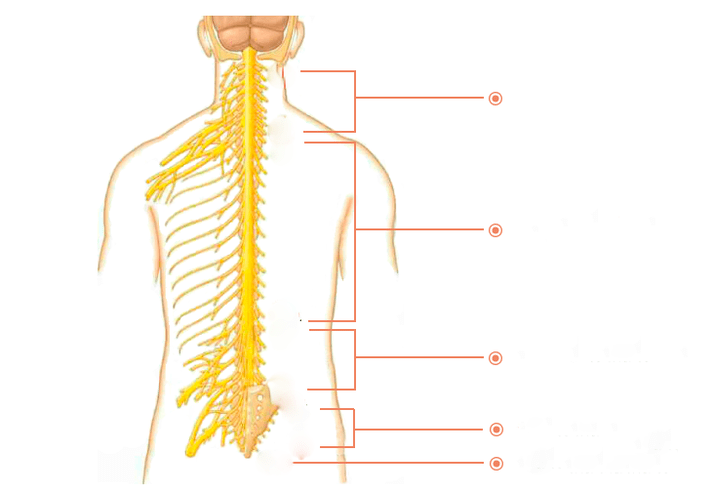
There are many nerves coming out of the spine. They are called spinal nerves. Each of these nerves branched off gradually, with well-defined boundaries along a certain area of the body. This area is called the segmental innervation area. Each vertebra, disc, nerve and region is numbered strictly correspondingly. If a nerve is affected, symptoms will appear in the segmental innervation corresponding to that nerve, not just anywhere—anywhere.
Aggressive symptoms include:
- Reduced or lost reflexes;
- breach of sensitivity;
- muscle weakness;
- Core pain.
thoracic innervation
Osteochondrosis D1–D2- Causes shoulder, collarbone and armpit pain.
Osteochondrosis D3–D6- Causes pain in upper chest, band-like features. Simulate heart pain, angina attack. In women, it can cause breast pain.
Osteochondrosis D7–D8- Causes low back pain at the level of the solar plexus. Simulate pain in the stomach, liver, gallbladder or pancreas. Reduces upper abdominal reflexes.
Osteochondrosis D9–D10- Causes hypochondriasis and upper abdominal pain. Sometimes it mimics what's called an "acute" belly -- severe pain in the abdomen. Decreased mid-abdominal reflex.
Osteochondrosis D11–D12- Causes pain in the groin area. Simulate the pain of female disease, appendicitis, intestinal disease. Lower abdominal reflexes.
reflex symptoms
Unlike nerve roots, reflex symptoms do not have clear boundaries. These may be: difficulty breathing, lack of air, pain on inhalation-exhalation, chills and "goose bumps" on the skin, intercostal neuralgia, chest girdle pain. Indigestion - worsening appetite, nausea, heartburn, bloating and stool disturbances are often noted. Due to pain, sleep is disturbed, and feelings of insomnia and lack of sleep occur. It's hard to move around, especially in the morning. The coordination of movements is disturbed - this is reflected in the gait. General weakness, weakness. Violations in the field of sex. irritability. Fatigue quickly. There are various types of pain. Chest tenderness. Pain between shoulder blades. Flank pain. Pain when raising arm. Pain when bending over or trying to straighten. Pain between shoulder blades. In general, pain in thoracic osteochondrosis can be divided into two types.
back pain- Moderately marked prolonged pain in the back and chest with periods of intensification and weakening.
dosago- Acute pain in the area "low back pain".
- Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis depend on the stage of osteochondrosis.
- Listlessness or trying to straighten up can aggravate their mood.
- Symptoms usually appear after age 35-45.
- It occurs about 3 times more frequently in women than in men.
Of course, you notice that the radicular symptoms are well defined and the reflex symptoms are very vague and nonspecific. As you know, everything that isn't clearly defined serves as a handy cover for professional helplessness. This applies, among other things, to reflex symptoms and physician-favorite concepts like "age-related changes. "Many of you are sure to be familiar with this situation when a doctor explains the problem through a "reflex" or "age-related" process. Most people rightly think at a time like this that the doctor simply can't figure out what's going on, and is trying to hide his incompetence in the fog of these "magic words".
There used to be a catchphrase: "Every accident has a first name, a last name, and a job title. " Every disease has its own unique symptoms. A doctor's job is to know them clearly. Then there's no need to let the fog fall and blame everything on thoracic osteochondrosis. Now you understand how important it is to find an experienced and knowledgeable doctor. Correct diagnosis and good treatment outcomes depend on this.
Diagnosis is the key to correct treatment
To date, there are many modern hardware diagnostic methods for osteochondrosis. The most accurate of these are MRI and CT. But the primary method remains clinical diagnosis -- which is when an experienced doctor compares data from at least three sources -- from the patient's complaints, MRI results and symptoms he finds during the exam. This allows you to make the most accurate diagnosis and develop an effective personal treatment plan.
treat
As you know, osteochondrosis is a real "tangle" symptom, untie it and your doctor will save you pain and suffering. But it is not possible to eliminate changes in the vertebrae and discs. Therefore, the term "treatment of osteochondrosis" must be properly understood. If you are interested in eliminating pain and other suffering, then yes - it is very possible. And if you have an academic discussion on the topic of restoring vertebrae and discs "like a newborn child", then no, the past cannot be returned to the past. You need to be realistic so you don't fall for the bait of scammers.
Don't fall for the bait of liars!
It is impossible for the vertebrae and intervertebral discs to return to their original shape!
What is the main treatment?
Soft manipulation therapy is the main method for the treatment of thoracic vertebral osteochondrosis. It's like an antibiotic for pneumonia - you can't live without it. Other types—massage, medication, physical therapy, and exercise therapy—are complementary.
How does gentle manual therapy work?
The nutrition of the intervertebral disc is directly related to the muscles surrounding the spine. In addition, the back muscles themselves are one of the causes of pain in thoracic osteochondrosis. Soft Manipulation is a special method that restores your muscles to their natural physiological state, eliminating spasms, muscle clamping and improving disc nutrition.
The disc is the only part of the body without blood vessels and is nourished by the normal functioning of the muscles.
Additionally, when treating with hands, chiropractors:
- Remove the load from the affected vertebrae and discs and distribute them correctly;
- relax muscles and help them return to normal;
thereby:
- Rescue the patient from the clip;
- Increase disk power;
- restore the body's motor function;
- Normalizes blood circulation.
Manual shocks mobilize the body's internal forces and initiate self-healing mechanisms.
Treatment is absolutely safe.
prevention
To avoid relapse, create comfortable sleeping and working conditions for yourself. Pay attention to your weight and proper nutrition. Keep your body active. But the most important thing is don't neglect your health and don't save money. Don't let things go by themselves. After recovery, try a maintenance period of gentle manual therapy at least once every three to six months - this will reduce risk factors. Don't forget that neglected osteochondrosis can lead to complications - herniated and herniated discs. Remember: your health comes first and foremost!
Running osteochondrosis can lead to complications - herniation and disc herniation.













































